9 Ways To Stop Bleeding Gums From Brushing Teeth


Is it normal to have bleeding gums from brushing or flossing? Why do so many people say that floss makes their gums bleed or see blood on their toothbrushes from time to time? Gum health is so important. Let's talk!
Why Do My Gums Bleed?
Bleeding gums aren’t normal. If your gums are bleeding whenever you’re doing something as routine as brushing your teeth, don’t try to solve the problem by not brushing that area; you’ll actually make the issue worse if you do.
Your immune system is basically causing inflammation by pushing antibodies to your infected gums. This thins out your gum tissues and makes them more sensitive. So, when there’s just a little bit of stimulation on the gum surface—like with a toothbrush or floss—they’re going to be more prone to bleeding. It’s probably not because you’re brushing your teeth too hard (although that’s a possibility.)
How To Stop Bleeding Gums When Brushing Teeth
In the majority of cases whenever dentists and hygienists see someone complaining about bleeding gums from brushing, we automatically assume it’s one of about a half dozen different things. Some are accidental or temporary, while others mean there’s an underlying issue going on that needs to be addressed before it gets any worse.
Look at it this way: if some other part of your body was just randomly bleeding every time you scrubbed your loofa over it in the shower, you would probably flip out. Just because your gums are bleeding and it seems fairly normal, it isn’t!
Here are 9 ways on how to stop bleeding gums:
1. Gingivitis
In 99% of cases where we see bleeding gums, it’s because of gingivitis. Gingivitis is your body’s response to plaque buildup next to the gums. Your body sees it as a bacterial infection, so it sends antibodies to that space and then your gums start to swell, feel tender, and bleed along the gum line when you brush or floss those spaces. Gingivitis usually makes the gums look red right next to the edges of the gums. It might be isolated in a certain hard-to-reach space or can be generalized throughout your mouth if you aren’t brushing as long or thoroughly as you ought to. Gingivitis leads to tooth decay and gum disease if you don't treat it properly.
Treatment
You can usually reverse poor dental hygiene and gingivitis within a couple of weeks if you’re brushing and flossing correctly. Brush for at least two minutes at a time to make sure you’re not rushing and skipping over too many spaces. Focus on just a couple of teeth at a time. Be sure to gently clean along your gumlines with your toothbrush every time you brush your teeth. Yes, it will bleed in the beginning. Flossing is also a must, because it gets between teeth and under the edges of your gums where a toothbrush won’t reach. If your bleeding gums don’t improve within a couple of weeks, you might have a more aggressive form of gum disease and require periodontal treatment.
2. Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease)
Periodontal disease or gum disease is a common cause of bleeding gums. As the infection progresses, the gums become inflamed, swollen and bleed easily when brushing or flossing. Bad bacteria in the plaque and tartar irritate the gums and cause them to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where more bacteria can grow. Eventually, the gum infection can lead to tooth loss and damage to the jawbone if left untreated.
Treatment
To prevent gum disease, deep cleanings are key to stopping the cycle of gum infection. Aggressive periodontal disease will need more than a scaling and root planing, though. Severe gum disease can lead to bone or gum grafting, antibiotic therapy, or laser tissue treatments may also be necessary.
2. Brushing Too Hard
Brushing harder is not better. It’s actually worse for your teeth the harder you brush. People who scrub their teeth too hard when they’re brushing tend to experience issues like gum recession and enamel abrasion (where the toothbrush actually wears away your enamel.) Their toothbrush bristles tend to look totally out whack, splayed out in every direction. Plus, when you brush that hard, you’re more likely to slip and jab yourself with your toothbrush, making your gums bleed.
Treatment
Practice good oral hygiene is always a good start. The best way to brush is to only apply just barely enough pressure to make your gum tissues blanch. Anything too hard to where your bristles are splayed over is too heavy. If you have a hard time lightening up on your toothbrush, try holding it with just three or four fingers instead of all five. Or switch to an electric brush and just hold it there so that it does all of the work for you. Make sure you’re angling the bristles toward your gums to make sure you’re targeting the areas where plaque tends to be the thickest.
3. Using The Wrong Toothbrush
What type of bristles does your toothbrush have? If it’s medium, hard, or extra-stiff, you’ve got the wrong one. Stiff bristles don’t flex and bend whenever you’re brushing the right way, so most of us instinctively scrub too hard and then inadvertently traumatize our gum tissues altogether.
Treatment
Definitely switch to a soft or extra-soft toothbrush. If you’re using an electric brush, let it do the work for you; there’s no need to scrub your teeth manually if you’ve got an electric brush that’s already vibrating thousands of times a second. Using a medium to stiff-bristled brush is not ever recommended. Unless of course you’re cleaning your bathroom tile or something like that. Harder, stiffer toothbrushes do not equal healthier, cleaner teeth.
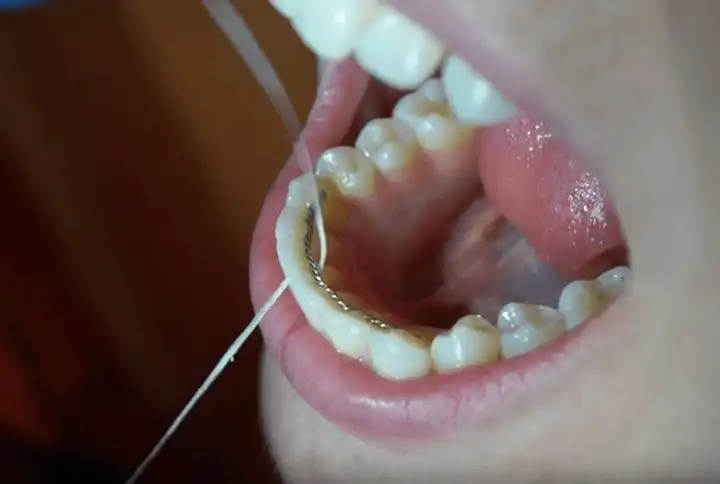
4. Floss Regularly
If you don’t floss every day, it’s just a matter of time before your gums will start to bleed. When you floss intermittently, there’s a good chance your gums will bleed every single time you do floss. Don’t worry; you are not cutting your gums and making them bleed. Usually, people floss once, see the blood, then stop flossing altogether. That’s actually the worst thing you could do. Pay attention to the inflammation and plaque levels and where they’re at, as opposed to worrying about if you’re hurting yourself with the floss.
Treatment
The best way to get rid of bleeding gums is to make sure you’re flossing around every tooth, every day, using the right technique. Wrap the dental floss in a “C” shape around the side of your tooth, then slide it up and down several times, including just under the edges of your gum. Lift it up and over the gums, then move to the next tooth. You. Need. To. Do. This. Every. Single. Day. In about two weeks, things should be better. You also have the option of using a water flosser and tracing along the edges of your gums—then pausing to clean between your teeth—instead of using traditional floss.
5. Poor Diet
If you eat a lot of processed foods and don’t get enough fresh fruits and vegetables, you’re more likely to have some type of nutritional deficiency. Plus, your gums need things like Omega-3, fiber, and firm textures of foods to stay healthy. Processed carbs and sugars usually mean more plaque buildup, which means more gum inflammation. Your mouth is the gateway to your body, so if your gum tissues don’t look healthy there’s a good chance that your insides won’t, either.
Treatment
Make sure you’re getting plenty of Omega-3s from things like fish, seeds, and nuts. Add fresh vegetables and fruits to your meals too. Anything crunchy like carrots or apples is a good choice. Be sure you’re eating plenty of leafy green vegetables, too. Opt for whole grains instead of processed, bleached flour if you’re eating bread or crackers. Talk to your doctor about additional supplements, but make it your goal to get all of the nutrients you need from a processed-free diet whenever possible.
6. Medications
Certain medications are known to increase the chances of bleeding gums, even if your mouth is fairly health. Over-the-counter drugs like aspirin and NSAIDs are a couple of examples. Other drugs—like the ones used for blood pressure or even birth control—tend to increase your risk of gum bleeding. Some of them, like calcium channel blockers, can cause “granuloma” like growths along your gums, too. When there are puffy areas like that, there are even more spaces for bacteria to hide and trigger gum irritation.
Treatment
Don’t give up your important medication regimen just because of bleeding gums, but definitely talk to your doctor about the issue. There might be alternatives. Be sure to provide your dentist with a list of any and all medications that you’re taking, as things like blood thinners could contraindicate a dental extraction or wisdom tooth removal. Your dental team will communicate with your medical provider to determine the best treatment approach.
7. Pregnancy Gingivitis
Expectant moms with pregnancy gingivitis will usually see a major flare-up in gingivitis symptoms throughout their entire mouth. Gums are puffy, tender, and bleed when brushing or flossing. In most cases, pregnancy gingivitis is a lot worse than traditional gingivitis, but there usually isn’t the bone loss that you’d see with traditional periodontal infections.
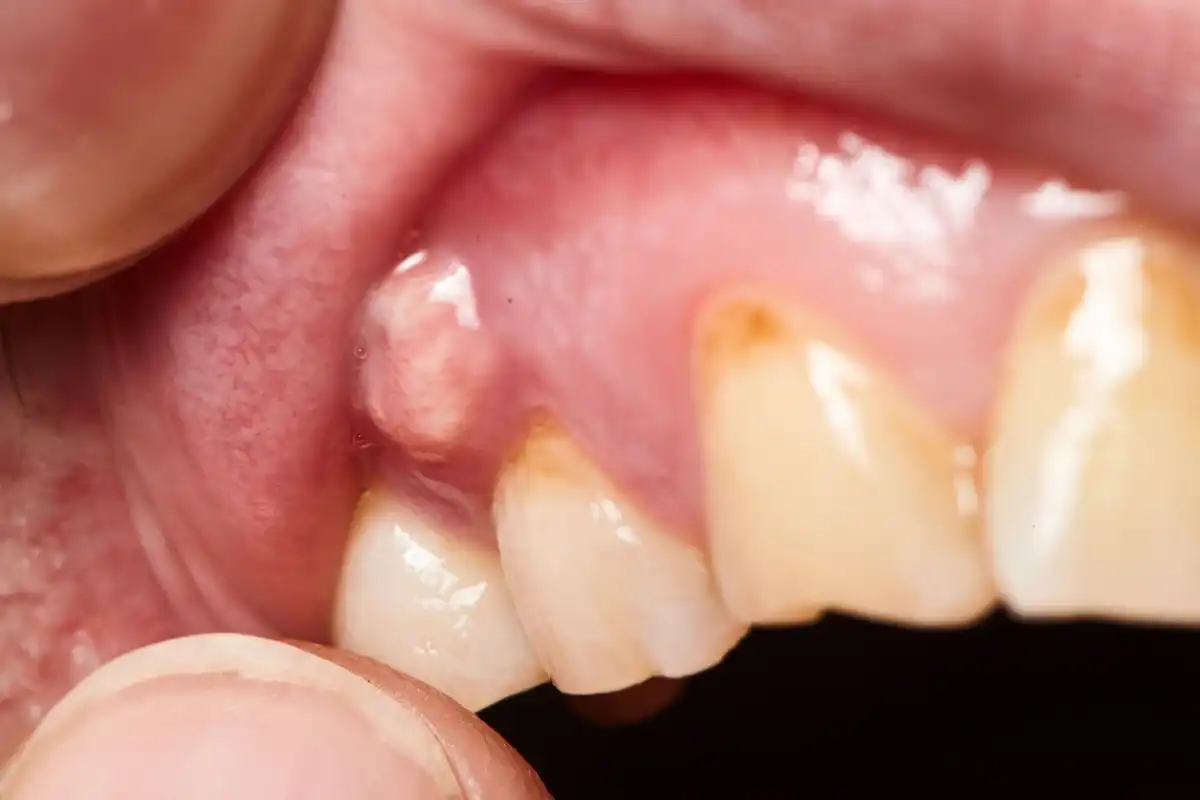
Some women with pregnancy gingivitis also see small bulbous growths along their gums, called “pregnancy tumors” or “pregnancy granulomas.” While they’re unsightly and sensitive, most will go away on their own.
Treatment
If you have pregnancy gingivitis, the best treatment is a combination of “watch and wait” with really good oral hygiene. When you physically remove the plaque around your teeth and gums, there’s less bacteria there to cause flare-ups with your body's immune system. Fortunately, most pregnancy gingivitis symptoms improve after giving birth, when your hormone levels start to stabilize again. The important thing is that you talk to your dentist to make sure you don’t have active periodontitis, because periodontal disease can pose a serious risk to your baby (there’s a higher risk of pre-eclampsia, pre-term birth rates, and stillbirths.)
8. Anemia
If you’re low on iron or have a known iron deficiency, there’s a good chance that your gums will bleed when you’re brushing and flossing, even if you have great oral hygiene! People with anemia also tend to have really pale or light-colored gum tissues. Some people even experience a swollen tongue or smooth surfaces across the top of their tongue.
Treatment
Make sure you’re getting enough iron through your diet and any supplements, as directed by your medical provider. Foods rich in iron include foods like red meats, dark green leafy veggies (like spinach,) and beans, among others can help alleviate bleeding gums.
How To Prevent Bleeding Gums When Flossing
The main thing to remember with flossing is that you don’t want it to cut straight down into your gums. Keep the floss curved tightly around one tooth at a time—flush up against the tooth—and rub up and down the side of the tooth as well as under the edges of the gums. Don’t force the floss under your gums, just let it slip down as far as it goes naturally, then stop right there.
When you’re flossing every day, you’re removing the bacteria under your gums that are responsible for triggering your immune response to promote gum healing. Keeping a cleaner space will prevent inflammation and bleeding from happening in the first place.
For those of you who absolutely loathe flossing, invest in a water flosser instead!
Talk With Your Dentist
How To Stop Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums are not normal. The faster you treat bleeding gums the sooner you improve gum health. If you’re seeing bleeding gums from brushing or flossing, it’s time to improve your oral hygiene routine and schedule a dental checkup. Once everything is nice and clean again—and you’ve adjusted the way you brush and floss—symptoms of bleeding gums will usually improve within 10-14 days. While some causes of bleeding gums are preventable and reversible, others aren’t. Don’t ignore the symptoms; after all, you wouldn’t if it was another part of your body!
Make your inbox smile!
Subscribe